Trigonometry
Worked Examples
Sine and Cosine Laws
We discussed trigonometric ratios in right-angle triangles in the first section. What about oblique triangles, i.e. those without a right angle? The sine and cosine laws presented below are trigonometric relations that hold for any triangle.Let $ABC$ be any triangle, labeled as below:
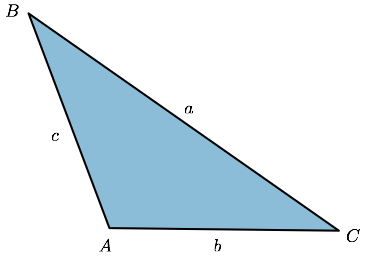
Labeling of a triangle
Part 1: The Sine Law
We have the following relation among the sides and angles of any triangle: $$\frac{\sin\left(A\right)}{a}=\frac{\sin\left(B\right)}{b}=\frac{\sin\left(C\right)}{c}$$Example. Given a triangle $ABC$ with $c=5$ cm, $A=45^{\circ}$ and $B=60^{\circ}$, find the length of $a$.
We know that $A+B+C=180^{\circ}$, so $C=180^{\circ}-45^{\circ}-60^{\circ}=75^{\circ}$.Using the Sine Law, $\frac{\sin\left(A\right)}{a} = \frac{\sin\left(C\right)}{c}$, we get: \begin{align*} \frac{\sin\left(45^{\circ}\right)}{a} &= \frac{\sin\left(75^{\circ}\right)}{5} = \frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{10\sqrt{2}} \\ \Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{a\sqrt{2}} &= \frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{10\sqrt{2}} \\ \Rightarrow \quad a &= \frac{10}{\sqrt{3}+1} \approx 3.66 \text{ cm} \end{align*}
